|
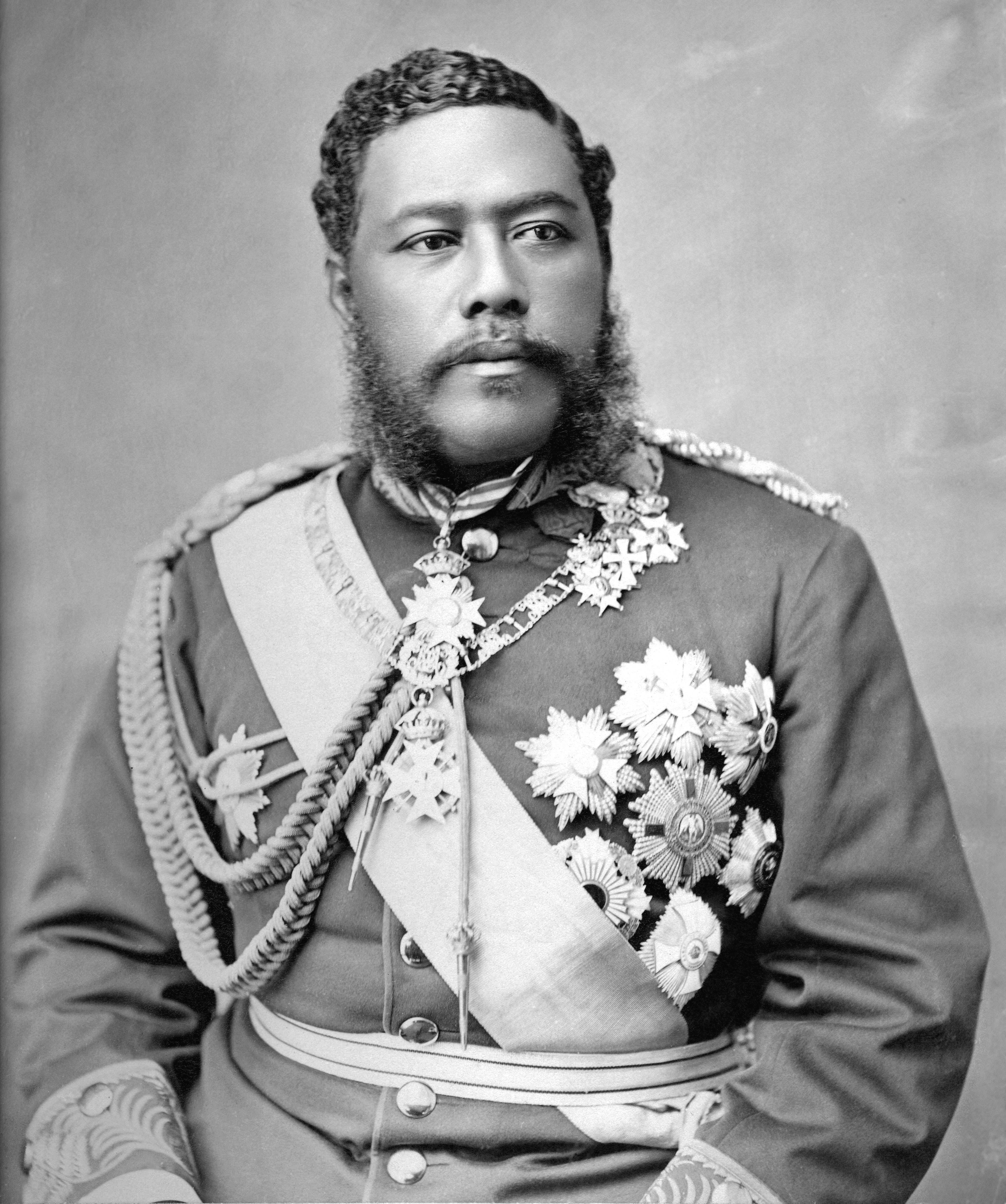
Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 – December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name was Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa Kalani Waiakua Kalanikau Iokikilo Kīwalaō i ke kapu Kamehameha when he ascended the throne. Under his reign, Hawaii evolved from an absolute monarchy to a constitutional monarchy with the signing of both the 1840 Constitution, which was the first Hawaiian Language Constitution, and the 1852 Constitution. He was the longest reigning monarch in the history of the Kingdom, ruling for 29 years and 192 days, although in the early part of his reign he was under a regency by Queen Kaahumanu and later by Kaahumanu II. His goal was the careful balancing of modernization by adopting Western ways while keeping his nation intact. Early life Kauikeaouli was born at Keauhou Bay, on Hawaii island, the largest islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oʻahu, Maui, Molokaʻi and Lānaʻi and unified them under one government. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauaʻi and Niʻihau joined the Hawaiian Kingdom voluntarily. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua. The kingdom won recognition from the major European powers. The United States became its chief trading partner and watched over it to prevent other powers (such as Britain and Japan) from asserting hegemony. In 1887 King Kalākaua was forced to accept a new constitution in a coup by the Honolulu Rifles, an anti-monarchist militia. Queen Liliʻuokalani, who succeeded Kalākaua in 1891, trie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keauhou Bay
Keauhou Bay is a historic area in the Kona District of the Big Island of Hawaii. The name comes from ''ke au hou'' which means "the new era" in the Hawaiian Language. Kamehameha III's Birthplace A small enclosure is maintained by the Daughters of Hawaii to mark the site of the birth of King Kamehameha III in 1814, the second son of Kamehameha I and Keopuolani. The early part of his reign he was under a regency by Kaʻahumanu. He was the longest reigning monarch in the Kingdom of Hawaii, until his death December 15, 1854. The site includes the Kauikeaouli stone (his birth name), added to the Hawaii register of historic places as site 10-37-4383 on January 13, 1978. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on July 24, 1978 as site 78001018. It is said Kauikeaouli was stillborn, but put on the stone by a visiting Kahuna where he was revived with a sacred chant. The Daughters of Hawaii held a ceremony marking the hundredth anniversary by placing a plaque with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Longest-reigning Monarchs
This is a list of the longest-reigning monarchs of all time, detailing the monarchs and lifelong leaders who have reigned the longest in world history, ranked by length of reign. Monarchs of sovereign states with verifiable reigns by exact date Twenty-five longest-reigning monarchs of states who were internationally recognized as sovereign for most or all of their reign. Monarchs of dependent or constituent states with verifiable reigns by exact date The table below contains 100 monarchs of states that were not internationally sovereign for most of their reign. Monarchs whose exact dates of rule are unknown These monarchs are grouped according to length of reign by year in whole numbers. Within each year-grouping, they appear in historical order. In a given year, there may have been a wide array of actual reign lengths based on days. Thus, this table does not present a precise ranking by length of reign. The list is limited to those that might reasonably be expec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1852 Constitution Of The Hawaiian Kingdom
The 1852 Constitution of the Hawaiian Kingdom, written in both English and Hawaiian, was constructed by King Kamehameha III. The purpose of its construction was to not only revise, but add to the 1840 Constitution in great length. The new constitution created a more democratic government much like those of the United States and Europe. King Kamehameha III The writer of the Hawaiian Constitution of 1852 was Kauikeaouli, referred to by the Hawaiian public as King Kamehameha III Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 – December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name is Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula K� .... He was the successor of Liholiho, King Kamehameha II. Kauikeaouli was the brother of Liholio and son of Kamehameha I. Kauikeaouli took over the throne at age eleven under the "regency" of his mother Ka'ahumanu. Kauikeaouli enacted the first constitution of Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1840 Constitution Of The Hawaiian Kingdom
The 1840 Constitution of the Hawaiian Kingdom titled was the first fully written constitution for the Hawaiian Kingdom. The need for a constitution was originally intended as a manner of laws set forth to control the Native Hawaiian population with a Western style and legal framework, giving less severe punishments, such as being exiled, than was the traditional custom until the 1840s. Christianity had failed to change many behaviors of the Hawaiian population, even with the support of the families. Adultery and many other sexual relations became forbidden. Hawaiians were arrested and sentenced to severe punishments that were not well organised. The exiled had little food and could easily swim away from the islands and the prison at Honolulu Fort. The issue became worse as fewer pardons from the were available, and the overall sentencing then became much more severe for the native population. Overview The constitution was enacted on October 8, 1840, by King Kamehameha III and K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies differ from absolute monarchies (in which a monarch is the only decision-maker) in that they are bound to exercise powers and authorities within limits prescribed by an established legal framework. Constitutional monarchies range from countries such as Liechtenstein, Monaco, Morocco, Jordan, Kuwait, and Bahrain, where the constitution grants substantial discretionary powers to the sovereign, to countries such as Australia, the United Kingdom, Canada, the Netherlands, Spain, Belgium, Sweden, Malaysia, Thailand, Cambodia, and Japan, where the monarch retains significantly less personal discretion in the exercise of their authority. ''Constitutional monarchy'' may refer to a system in which the monarch acts as a non-party political head of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constitution may exist in some countries. These are often hereditary monarchies. On the other hand, in constitutional monarchies, in which the authority of the head of state is also bound or restricted by the constitution, a legislature, or unwritten customs, the king or queen is not the only one to decide, and their entourage also exercises power, mainly the prime minister. Absolute monarchy in Europe declined substantially following the French Revolution and World War I, both of which led to the popularization of theories of government based on the notion of popular sovereignty. Absolute monarchies include Brunei, Eswatini, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Vatican City, and the individual emirates composing the United Arab Emirates, which itself is a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Kingdom
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaii (island), Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oahu, Oʻahu, Maui, Molokai, Molokaʻi and Lanai, Lānaʻi and unified them under one government. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unification of Hawaii, unified when Kauai, Kauaʻi and Niihau, Niʻihau joined the Hawaiian Kingdom voluntarily. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua. The kingdom won recognition from the major European powers. The United States became its chief trading partner and Hawaiian Kingdom–United States relations, watched over it to Monroe Doctrine, prevent other powers (such as British Empire, Britain and Empire of Japan, Japan) from asserting hegemony. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauna Ala , cinder cone of Haleakalā
{{disambig ...
Mauna or Mouna may refer to: * ''Mauna'' (moth), genus of moths in the family Geometridae * Mauna (silence), silence in Hindu philosophy * Mauna, Käbschütztal, village in Käbschütztal, Germany * A Hawaiian word for mountain, used in the following Hawaiian volcano names: ** Mauna Loa, on Hawai'i ** Mauna Kea, on Hawai'i ** Mauna Ulu, cinder cone of Kīlauea, on Hawai'i ** Mauna Iki, cinder cone of Kīlauea, on Hawai'i ** Mauna Haleakalā, on Maui ** Mauna Hina Mauna or Mouna may refer to: * ''Mauna'' (moth), genus of moths in the family Geometridae * Mauna (silence), silence in Hindu philosophy * Mauna, Käbschütztal, village in Käbschütztal, Germany * A Hawaiian word for mountain, used in the follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Society
The Polynesian Society is a non-profit organisation based at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, dedicated to the scholarly study of the history, ethnography, and mythology of Oceania. History The society was co-founded in 1892 by Percy Smith and Edward Tregear, largely in response to a conviction, widely held at the time, that the Māori and other Polynesian peoples were a dying race. Smith and his friends hoped that it would help to preserve the traditional lore of the Māori before it disappeared and provide scholars with a forum for learned discussion of their ethnographic research (Byrnes 2006). The initial membership of the society was 112, which had grown to 1,300 by 1965. Presidents have included bishops H. W. and W. L. Williams; James Pope, Edward Tregear, Percy Smith, Elsdon Best, William Skinner, Sir Āpirana Ngata, Harry Skinner, J. M. McEwen, Professor Sir Hugh Kawharu and Dame Joan Metge. The present president is Dr Richard Benton. Until her death in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
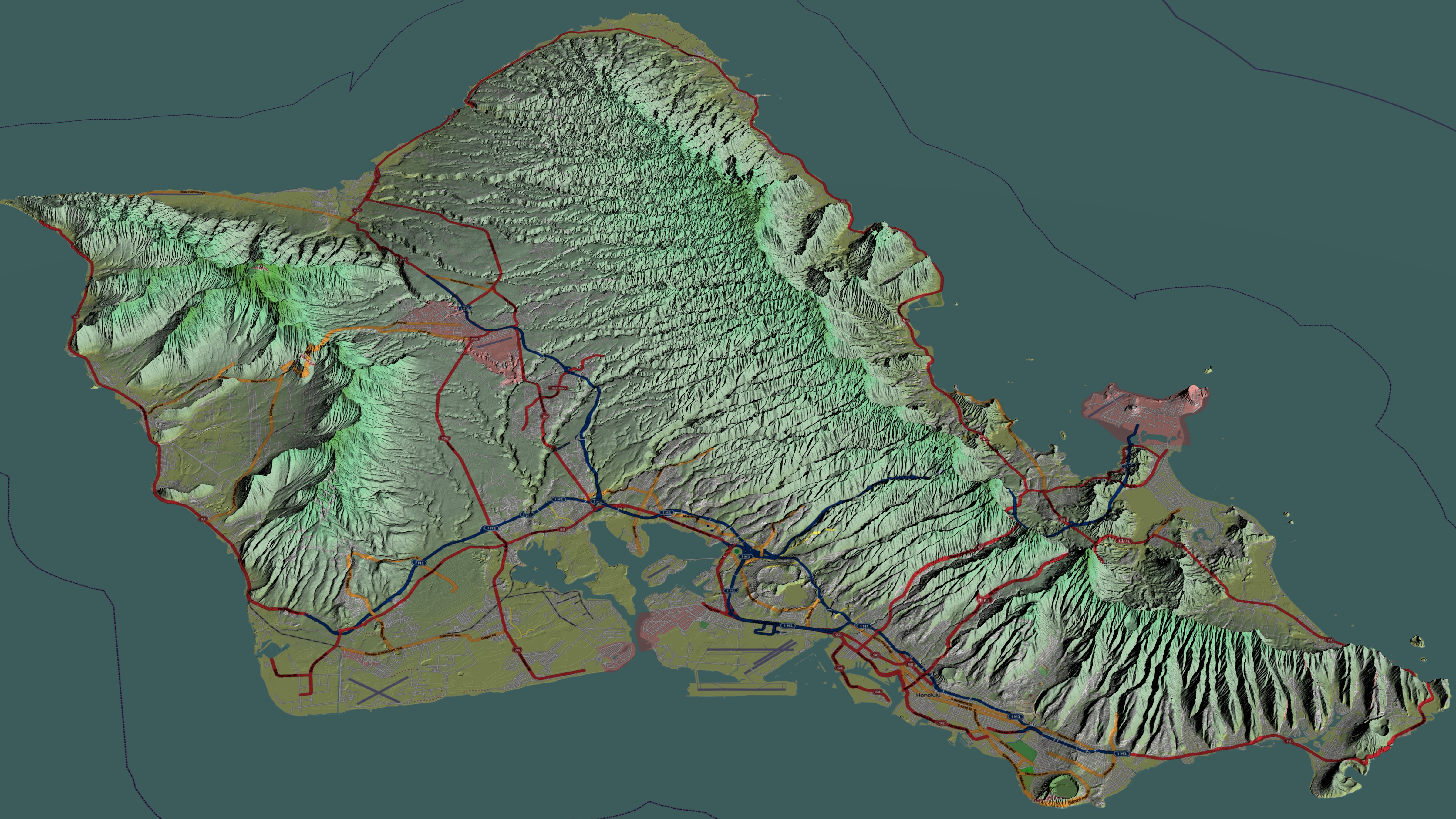
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian islands, Hawaiian Island, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions. ''Honolulu'' means "sheltered harbor" or "calm port" in Hawaiian; its old name, ''Kou'', roughly encompasses the area from Nuuanu Avenue to Alakea Street and from Hotel Street to Queen Street, which is the heart of the present downtown district. The city's desirability as a port accounts for its historical growth and importance in the Hawaiian archipelago and the broader P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Kamehameha_III%2C_1825.jpg)